- (Topic 23)
In which part of OSI layer, ARP Poisoning occurs?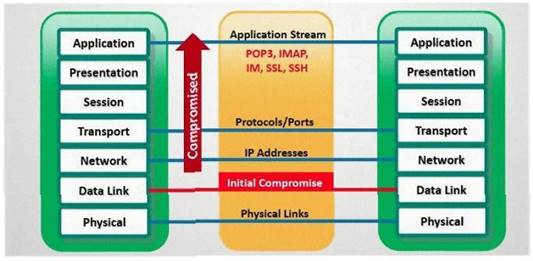
Correct Answer:B
- (Topic 23)
Why attackers use proxy servers?
Correct Answer:D
- (Topic 3)
The FIN flag is set and sent from host A to host B when host A has no more data to transmit (Closing a TCP connection). This flag releases the connection resources. However, host A can continue to receive data as long as the SYN sequence number of transmitted packets from host B are lower than the packet segment containing the set FIN flag.
Correct Answer:A
For sequence number purposes, the SYN is considered to occur before the first actual data octet of the segment in which it occurs, while the FIN is considered to occur after the last actual data octet in a segment in which it occurs. So packets receiving out of order will still be accepted.
- (Topic 19)
Exhibit: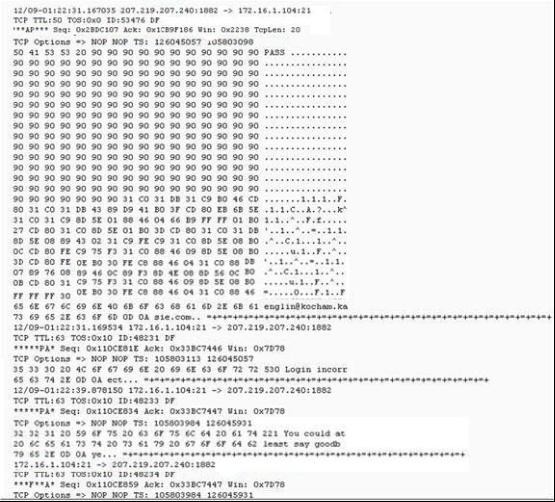
Given the following extract from the snort log on a honeypot, what service is being exploited? :
Correct Answer:A
The connection is done to 172.16.1.104:21.
- (Topic 23)
When a normal TCP connection starts, a destination host receives a SYN (synchronize/start) packet from a source host and sends back a SYN/ACK (synchronize acknowledge). The destination host must then hear an ACK (acknowledge) of the
SYN/ACK before the connection is established. This is referred to as the "TCP three-way handshake." While waiting for the ACK to the SYN ACK, a connection queue of finite size on the destination host keeps track of connections waiting to be completed. This queue typically empties quickly since the ACK is expected to arrive a few milliseconds after the SYN ACK. How would an attacker exploit this design by launching TCP SYN attack?
Correct Answer:B