- (Exam Topic 6)
You have an Azure App Service plan that hosts an Azure App Service named App1. You configure one production slot and four staging slots for App1.
You need to allocate 10 percent of the traffic to each staging slot and 60 percent of the traffic to the production slot.
What should you add to Appl1?
Correct Answer:A
Besides swapping, deployment slots offer another killer feature: testing in production. Just like the name suggests, using this, you can actually test in production. This means that you can route a specific percentage of user traffic to one or more of your deployment slots.
Example: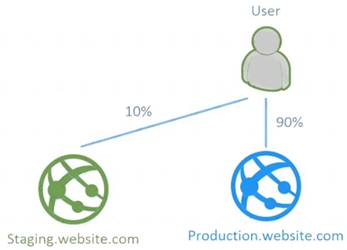
References:
https://stackify.com/azure-deployment-slots/
- (Exam Topic 5)
You have two Azure virtual networks named VNet1 and VNet2. VNet1 contains an Azure virtual machine named VM1. VNet2 contains an Azure virtual machine named VM2.
VM1 hosts a frontend application that connects to VM2 to retrieve data. Users report that the frontend application is slower than usual.
You need to view the average round-trip time (RTT) of the packets from VM1 to VM2. Which Azure Network Watcher feature should you use?
Correct Answer:D
The Connection Monitor feature in Azure Network Watcher is now generally available in all public regions. Connection Monitor provides you RTT values on a per-minute granularity. You can monitor a direct TCP connection from a virtual machine to a virtual machine, FQDN, URI, or IPv4 address.
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/updates/general-availability-azure-network-watcher-connection-monitor-in-all
- (Exam Topic 5)
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
You deploy a Linux virtual machine named VM1 to Subscription1. You need to monitor the metrics and the logs of VM1.
What should you use?
Correct Answer:A
You can use extensions to configure diagnostics on your VMs to collect additional metric data.
The basic host metrics are available, but to see more granular and VM-specific metrics, you need to install the Azure diagnostics extension on the VM. The Azure diagnostics extension allows additional monitoring and diagnostics data to be retrieved from the VM.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/tutorial-monitor
- (Exam Topic 6)
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.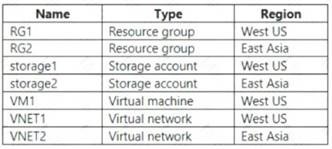
VM1 connects to VNET1.
You need to connect VM1 to VNET2.
Solution: You delete VM1. You recreate VM1, and then you create a new network interface for VM1 and connect it to VNET2.
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:B
- (Exam Topic 5)
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.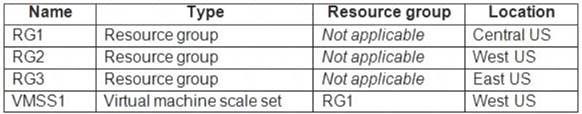
VMSS1 is set to VM (virtual machines) orchestration mode.
You need to deploy a new Azure virtual machine named VM1, and then add VM1 to VMSS1.
Which resource group and location should you use to deploy VM1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.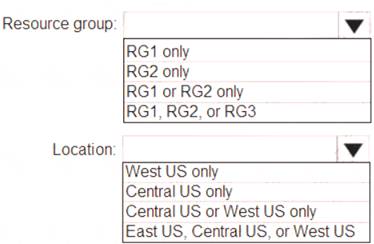
Solution:
Box 1: RG1, RG2, or RG3
The resource group stores metadata about the resources. When you specify a location for the resource group, you're specifying where that metadata is stored.
Box 2: West US only
Note: Virtual machine scale sets will support 2 distinct orchestration modes:
ScaleSetVM – Virtual machine instances added to the scale set are based on the scale set configuration model. The virtual machine instance lifecycle - creation, update, deletion - is managed by the scale set.
VM (virtual machines) – Virtual machines created outside of the scale set can be explicitly added to the scaleset.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/management/overview
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A