A security engineer is working on a large software development project. As part of the design of the project, various stakeholder requirements were gathered and decomposed to an implementable and testable level. Various security requirements were also documented.
Organize the following security requirements into the correct hierarchy required for an SRTM. Requirement 1: The system shall provide confidentiality for data in transit and data at rest. Requirement 2: The system shall use SSL, SSH, or SCP for all data transport.
Requirement 3: The system shall implement a file-level encryption scheme. Requirement 4: The system shall provide integrity for all data at rest. Requirement 5: The system shall perform CRC checks on all files.
Correct Answer:B
Confidentiality and integrity are two of the key facets of data security. Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is not disclosed to unauthorized users; while integrity ensures that data is not altered by unauthorized users. These are Level 1 requirements.
Confidentiality is enforced through encryption of data at rest, encryption of data in transit, and access control. Encryption of data in transit is accomplished by using secure protocols such as PSec, SSL, PPTP, SSH, and SCP, etc.
Integrity can be enforced through hashing, digital signatures and CRC checks on the files. In the SRTM hierarchy, the enforcement methods would fall under the Level requirement. References:
Gregg, Michael, and Billy Haines, CASP CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner Study Guide, John Wiley & Sons, Indianapolis, 2012, pp. 17-19, 20, 27-29
Which of the following describes a risk and mitigation associated with cloud data storage?
Correct Answer:A
With cloud data storage, the storage provider will have large enterprise SANs providing large pools of storage capacity. Portions of the storage pools are assigned to customers. The risk is that multiple customers are storing their data on the same physical hardware storage devices. This presents a risk (usually a very small risk, but a risk all the same) of other customers using the same cloud storage hardware being able to view your data.
The mitigation of the risk is to encrypt your data stored on the SAN. Then the data would be unreadable even if another customer was able to access it.
Incorrect Answers:
B: Offsite replication is used for disaster recovery purposes. It is not considered to be a risk as long as the data is secure in the other site. Multi-site backups are not a risk mitigation.
C: Data loss from de-duplication is not considered to be a risk. De-duplication removes duplicate copies of data to reduce the storage space required for the dat
A. Dynamic host bus addressing is not a risk mitigation.
D: Combined data archiving is not considered to be a risk. The archived data would be less accessible to other customers than the live data on the shared storage.
Following a merger, the number of remote sites for a company has doubled to 52. The company has decided to secure each remote site with an NGFW to provide web filtering, NIDS/NIPS, and network antivirus. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) has requested that the security engineer provide recommendations on sizing for the firewall with the requirements that it be easy to manage and provide capacity for growth.
The tables below provide information on a subset of remote sites and the firewall options: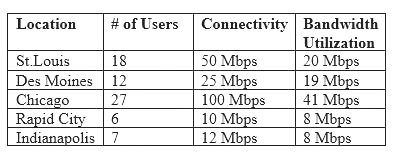
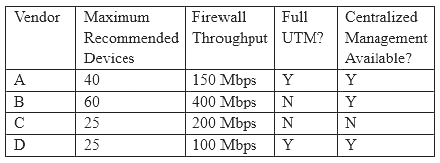
Which of the following would be the BEST option to recommend to the CIO?
Correct Answer:D
A security incident responder discovers an attacker has gained access to a network and has overwritten key system files with backdoor software. The server was reimaged and patched offline. Which of the following tools should be implemented to detect similar attacks?
Correct Answer:CD