A network engineer must ensure that always-on VPN access is enabled Curt restricted to company assets Which of the following best describes what the engineer needs to do''
Correct Answer:A
To ensure always-on VPN access is enabled and restricted to company assets, the network engineer needs to generate device certificates using the specific template settings required for the company's VPN solution. These certificates ensure that only authorized devices can establish a VPN connection.
Why Device Certificates are Necessary:
✑ Authentication: Device certificates authenticate company assets, ensuring that only authorized devices can access the VPN.
✑ Security: Certificates provide a higher level of security compared to username and password combinations, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
✑ Compliance: Certificates help in meeting security policies and compliance requirements by ensuring that only managed devices can connect to the corporate network.
Other options do not provide the same level of control and security for always-on VPN access:
✑ B. Modify signing certificates for IKE version 2: While important for VPN protocols,
it does not address device-specific authentication.
✑ C. Create a wildcard certificate: This is not suitable for device-specific authentication and could introduce security risks.
✑ D. Add the VPN hostname as a SAN entry: This is more related to certificate management and does not ensure device-specific authentication.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
✑ "Device Certificates for VPN Access," Cisco Documentation
✑ NIST Special Publication 800-77, "Guide to IPsec VPNs"
A company plans to implement a research facility with Intellectual property data that should be protected The following is the security diagram proposed by the security architect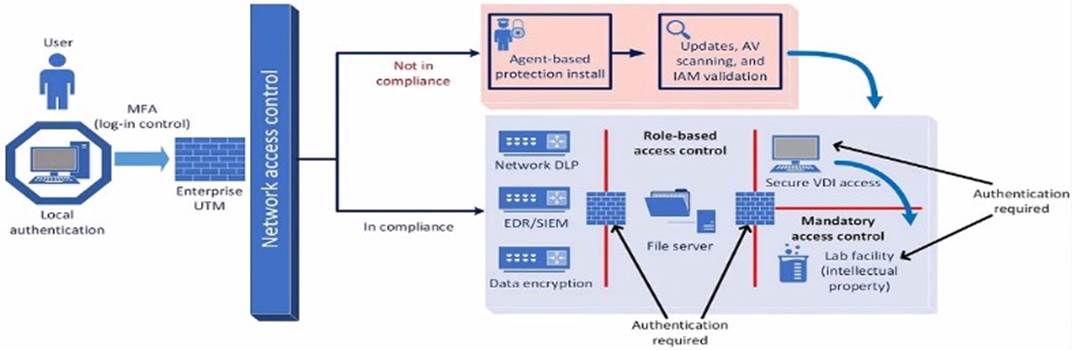
Which of the following security architect models is illustrated by the diagram?
Correct Answer:D
The security diagram proposed by the security architect depicts a Zero Trust security model. Zero Trust is a security framework that assumes all entities, both inside and outside the network, cannot be trusted and must be verified before gaining access to resources.
Key Characteristics of Zero Trust in the Diagram:
✑ Role-based Access Control: Ensures that users have access only to the resources necessary for their role.
✑ Mandatory Access Control: Additional layer of security requiring authentication for access to sensitive areas.
✑ Network Access Control: Ensures that devices meet security standards before accessing the network.
✑ Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
This model aligns with the Zero Trust principles of never trusting and always verifying access requests, regardless of their origin.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
✑ NIST Special Publication 800-207, "Zero Trust Architecture"
✑ "Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture," Forrester Research
After an incident response exercise, a security administrator reviews the following table: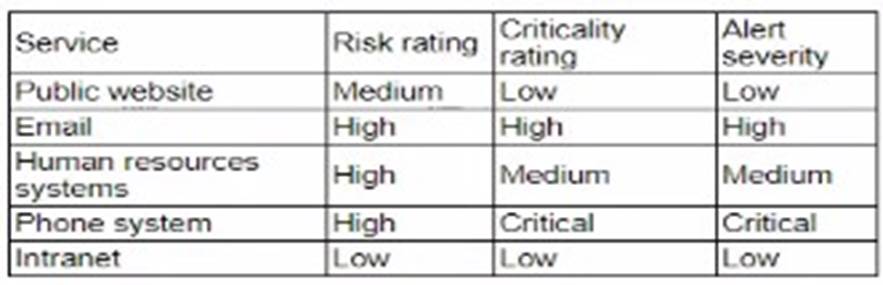
Which of the following should the administrator do to beat support rapid incident response in the future?
Correct Answer:B
Enabling dashboards for service status monitoring is the best action to support rapid incident response. The table shows various services with different risk, criticality, and alert severity ratings. To ensure timely and effective incident response, real-time visibility into the status of these services is crucial.
Why Dashboards for Service Status Monitoring?
✑ Real-time Visibility: Dashboards provide an at-a-glance view of the current status of all critical services, enabling rapid detection of issues.
✑ Centralized Monitoring: A single platform to monitor the status of multiple services helps streamline incident response efforts.
✑ Proactive Alerting: Dashboards can be configured to show alerts and anomalies immediately, ensuring that incidents are addressed as soon as they arise.
✑ Improved Decision Making: Real-time data helps incident response teams make informed decisions quickly, reducing downtime and mitigating impact.
Other options, while useful, do not offer the same level of comprehensive, real-time visibility and proactive alerting:
✑ A. Automate alerting to IT support for phone system outages: This addresses one
service but does not provide a holistic view.
✑ C. Send emails for failed log-in attempts on the public website: This is a specific alert for one type of issue and does not cover all services.
✑ D. Configure automated isolation of human resources systems: This is a reactive measure for a specific service and does not provide real-time status monitoring.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
✑ NIST Special Publication 800-61 Revision 2, "Computer Security Incident Handling Guide"
✑ "Best Practices for Implementing Dashboards," Gartner Research