Refer to the exhibits.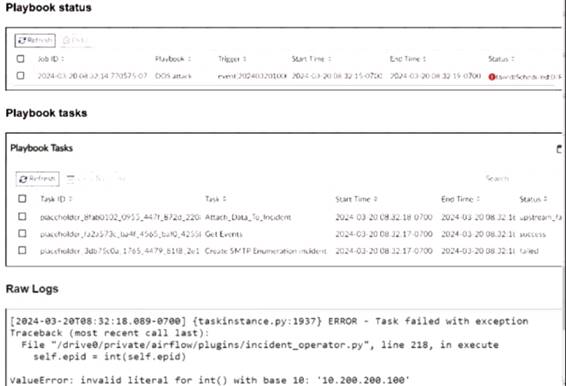
The DOS attack playbook is configured to create an incident when an event handler generates a denial-of-ser/ice (DoS) attack event.
Why did the DOS attack playbook fail to execute?
Correct Answer:A
Understanding the Playbook and its Components:
The exhibit shows the status of a playbook named "DOS attack" and its associated tasks.
The playbook is designed to execute a series of tasks upon detecting a DoS attack event.
Analysis of Playbook Tasks:
Attach_Data_To_Incident:Task ID placeholder_8fab0102, status is "upstream_failed," meaning it did not execute properly due to a previous task's failure.
Get Events:Task ID placeholder_fa2a573c, status is "success."
Create SMTP Enumeration incident:Task ID placeholder_3db75c0a, status is "failed."
Reviewing Raw Logs:
The error log shows aValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '10.200.200.100'.
This error indicates that the task attempted to convert a string (the IP address '10.200.200.100') to an integer, which is not possible.
Identifying the Source of the Error:
The error occurs in the file "incident_operator.py," specifically in theexecutemethod.
This suggests that the task "Create SMTP Enumeration incident" is the one causing the issue because it failed to process the data type correctly.
Conclusion:
The failure of the playbook is due to the "Create SMTP Enumeration incident" task receiving a string value (an IP address) when it expects an integer value. This mismatch in data types leads to the error.
References:
Fortinet Documentation on Playbook and Task Configuration.
Python error handling documentation for understandingValueError.
When does FortiAnalyzer generate an event?
Correct Answer:C
Understanding Event Generation in FortiAnalyzer:
FortiAnalyzer generates events based on predefined rules and conditions to help in monitoring and responding to security incidents.
Analyzing the Options:
Option A:Data selectors filter logs based on specific criteria but do not generate events on their own.
Option B:Connectors facilitate integrations with other systems but do not generate events based on log matches.
Option C:Event handlers are configured with rules that define the conditions under which events are generated. When a log matches a rule in an event handler, FortiAnalyzer generates an event.
Option D:Tasks in playbooks execute actions based on predefined workflows but do not directly generate events based on log matches.
Conclusion:
FortiAnalyzer generates an event when a log matches a rule in an event handler.
References:
Fortinet Documentation on Event Handlers and Event Generation in FortiAnalyzer.
Best Practices for Configuring Event Handlers in FortiAnalyzer.
Refer to Exhibit: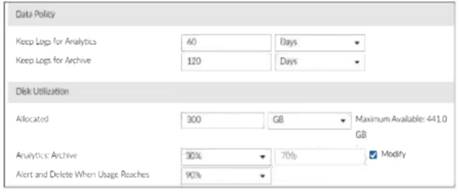
You are tasked with reviewing a new FortiAnalyzer deployment in a network with multiple registered logging devices. There is only one FortiAnalyzer in the topology.
Which potential problem do you observe?
Correct Answer:B
Understanding FortiAnalyzer Data Policy and Disk Utilization:
FortiAnalyzer uses data policies to manage log storage, retention, and disk utilization.
The Data Policy section indicates how long logs are kept for analytics and archive purposes.
The Disk Utilization section specifies the allocated disk space and the proportions used for analytics and archive, as well as when alerts should be triggered based on disk usage.
Analyzing the Provided Exhibit:
Keep Logs for Analytics:60 Days
Keep Logs for Archive:120 Days
Disk Allocation:300 GB (with a maximum of 441 GB available)
Analytics: Archive Ratio:30% : 70%
Alert and Delete When Usage Reaches:90%
Potential Problems Identification:
Disk Space Allocation:The allocated disk space is 300 GB out of a possible 441 GB, which might not be insufficient if the log volume is high, but it is not the primary concern based on the given data.
Analytics-to-Archive Ratio:The ratio of 30% for analytics and 70% for archive is unconventional. Typically, a higher percentage is allocated for analytics since real-time or recent data analysis is often prioritized. A common configuration might be a 70% analytics and 30% archive ratio. The misconfigured ratio can lead to insufficient space for analytics, causing issues with real-time monitoring and analysis.
Retention Periods:While the retention periods could be seen as lengthy, they are not necessarily indicative of a problem without knowing the specific log volume and compliance requirements. The length of these periods can vary based on organizational needs and legal requirements.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, the primary issue observed is theanalytics-to-archive ratiobeing misconfigured. This misconfiguration can significantly impact the effectiveness of the FortiAnalyzer in real-time log analysis, potentially leading to delayed threat detection and response.
References:
Fortinet Documentation on FortiAnalyzer Data Policies and Disk Management.
Best Practices for FortiAnalyzer Log Management and Disk Utilization.
Refer to the exhibit,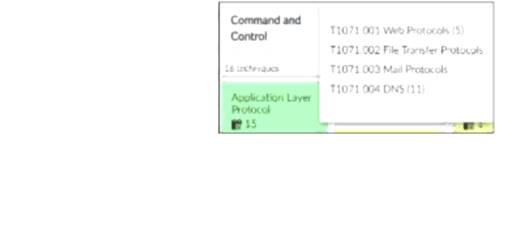
which shows the partial output of the MITRE ATT&CK Enterprise matrix on FortiAnalyzer. Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BC
Understanding the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix:
The MITRE ATT&CK framework is a knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations.
Each tactic in the matrix represents the "why" of an attack technique, while each technique represents "how" an adversary achieves a tactic.
Analyzing the Provided Exhibit:
The exhibit shows part of the MITRE ATT&CK Enterprise matrix as displayed on FortiAnalyzer.
The focus is on technique T1071 (Application Layer Protocol), which has subtechniques labeled T1071.001, T1071.002, T1071.003, and T1071.004.
Each subtechnique specifies a different type of application layer protocol used for Command and Control (C2):
T1071.001 Web Protocols
T1071.002 File Transfer Protocols
T1071.003 Mail Protocols
T1071.004 DNS
Identifying Key Points:
Subtechniques under T1071:There are four subtechniques listed under the primary technique T1071, confirming that statement B is true.
Event Handlers for T1071:FortiAnalyzer includes event handlers for monitoring various tactics and techniques. The presence of event handlers for tactic T1071 suggests active monitoring and alerting for these specific subtechniques, confirming that statement C is true.
Misconceptions Clarified:
Statement A (four techniques under tactic T1071) is incorrect because T1071 is a single technique with four subtechniques.
Statement D (15 events associated with the tactic) is misleading. The number 15 refers to the techniques under the Application Layer Protocol, not directly related to the number of events.
Conclusion:
The accurate interpretation of the exhibit confirms that there are four subtechniques under technique T1071 and that there are event handlers covering tactic T1071.
References:
MITRE ATT&CK Framework documentation.
FortiAnalyzer Event Handling and MITRE ATT&CK Integration guides.
A customer wants FortiAnalyzer to run an automation stitch that executes a CLI command on FortiGate to block a predefined list of URLs, if a botnet command-and-control (C&C) server IP is detected.
Which FortiAnalyzer feature must you use to start this automation process?
Correct Answer:C
Understanding Automation Processes in FortiAnalyzer:
FortiAnalyzer can automate responses to detected security events, such as running commands on FortiGate devices.
Analyzing the Customer Requirement:
The customer wants to run a CLI command on FortiGate to block predefined URLs when a botnet C&C server IP is detected.
This requires an automated response triggered by a specific event.
Evaluating the Options:
Option A:Playbooks orchestrate complex workflows but are not typically used for direct event-triggered automation processes.
Option B:Data selectors filter logs based on criteria but do not initiate automation processes.
Option C:Event handlers can be configured to detect specific events (such as detecting a botnet C&C server IP) and trigger automation stitches to execute predefined actions.
Option D:Connectors facilitate communication between FortiAnalyzer and other systems but are not the primary mechanism for initiating automation based on log events.
Conclusion:
To start the automation process when a botnet C&C server IP is detected, you must use anEvent handlerin FortiAnalyzer.
References:
Fortinet Documentation on Event Handlers and Automation Stitches in FortiAnalyzer.
Best Practices for Configuring Automated Responses in FortiAnalyzer.