What are two requirements for an IP fabric? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AB
AnIP fabricis a network architecture commonly used in data centers to provide scalable, high-throughput connectivity using aspine-leaf topology.
Step-by-Step Breakdown: Layer 3 Routing Protocol:An IP fabric relies on aLayer 3 routing protocol, typically BGP or OSPF, to provide routing between the leaf and spine switches. This ensures efficient traffic forwarding across the network.
Layer 3 Routing Protocol:An IP fabric relies on aLayer 3 routing protocol, typically BGP or OSPF, to provide routing between the leaf and spine switches. This ensures efficient traffic forwarding across the network. Single Connection Between Spine and Leaf:In an IP fabric, each leaf switch connects toevery spine switchwith a single connection. This ensures that traffic between any two leaf switches can travel through the spine layer in just two hops.
Single Connection Between Spine and Leaf:In an IP fabric, each leaf switch connects toevery spine switchwith a single connection. This ensures that traffic between any two leaf switches can travel through the spine layer in just two hops.
Juniper Reference: Spine-Leaf Design: Juniper??s IP fabric implementations are designed for scalability and low-latency routing, often using protocols like BGP for Layer 3 control.
Spine-Leaf Design: Juniper??s IP fabric implementations are designed for scalability and low-latency routing, often using protocols like BGP for Layer 3 control.
Which statement is correct about areas in OSPF?
Correct Answer:C
InOSPF (Open Shortest Path First), areas are used to segment a network into smaller, more manageable pieces to improve scalability. By dividing a network into areas, OSPF can reduce the size of thelink-state database (LSDB), which helps routers process updates more efficiently.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Purpose of OSPF Areas:OSPF areas allow for hierarchical routing within the OSPF domain. Routers in the same area have identical LSDBs, but routers in different areas do not exchange full link-state information. Instead, they exchange summarized routes, which reduces the LSDB size and CPU/memory usage.
Benefits:Reducing the LSDB size improves scalability and ensures faster convergence in larger networks. Area 0 is the backbone area, and all other areas must connect to it, forming a hierarchical structure.
Juniper Reference:
OSPF Configuration: Areas in OSPF are configured to optimize network performance by limiting the scope of link-state advertisements (LSAs) to within an area.
Which statement is correct about aggregate routes?
Correct Answer:D
An aggregate route is a summarized route that is created by combining multiple specific routes into a single, broader route. In Junos OS, when an aggregate route is configured, its default next hop is set toreject.
Step-by-Step Explanation:: Aggregate Route:Aggregate routes are used to reduce the size of routing tables by representing a collection of more specific routes with a single summary route. They help improve routing efficiency and scalability, especially in large networks.
Aggregate Route:Aggregate routes are used to reduce the size of routing tables by representing a collection of more specific routes with a single summary route. They help improve routing efficiency and scalability, especially in large networks. Default Next Hop Behavior:
Default Next Hop Behavior: When you configure an aggregate route in Junos OS, it has arejectnext hop by default.
When you configure an aggregate route in Junos OS, it has arejectnext hop by default. Therejectnext hop means that if a packet matches the aggregate route but there is no more specific route in the routing table for that destination, the packet will be discarded, and an ICMP "destination unreachable" message is sent to the source.
Therejectnext hop means that if a packet matches the aggregate route but there is no more specific route in the routing table for that destination, the packet will be discarded, and an ICMP "destination unreachable" message is sent to the source. This behavior helps to prevent routing loops and ensures that traffic isn't forwarded to destinations for which there is no valid route.
This behavior helps to prevent routing loops and ensures that traffic isn't forwarded to destinations for which there is no valid route. Modifying Next Hop:If needed, the next hop behavior of an aggregate route can be changed todiscard (which silently drops the packet) or to another specific next hop. However, by default, the next hop is set toreject.
Modifying Next Hop:If needed, the next hop behavior of an aggregate route can be changed todiscard (which silently drops the packet) or to another specific next hop. However, by default, the next hop is set toreject.
Juniper Reference: Junos Command: set routing-options aggregate route
Junos Command: set routing-options aggregate route  Verification: Use show route to verify the presence and behavior of aggregate routes.
Verification: Use show route to verify the presence and behavior of aggregate routes.
What is the behavior of the default export policy for OSPF?
Correct Answer:B
In Junos, thedefault export policyforOSPFis toreject all routesfrom being exported.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Default Export Policy:By default,OSPFin Junos does not export any routes to other routing protocols or neighbors. This is a safety mechanism to prevent unintended route advertisements.
Custom Export Policies:
If you need to export routes, you must create a customexport policythat explicitly defines which routes to advertise.
Example: You can create an export policy to redistribute static or connected routes into OSPF.
Juniper Reference:
OSPF Export Behavior: In Juniper devices, the default policy for OSPF is to reject route advertisements unless explicitly configured otherwise through custom policies.
You are troubleshooting a downed BGP session.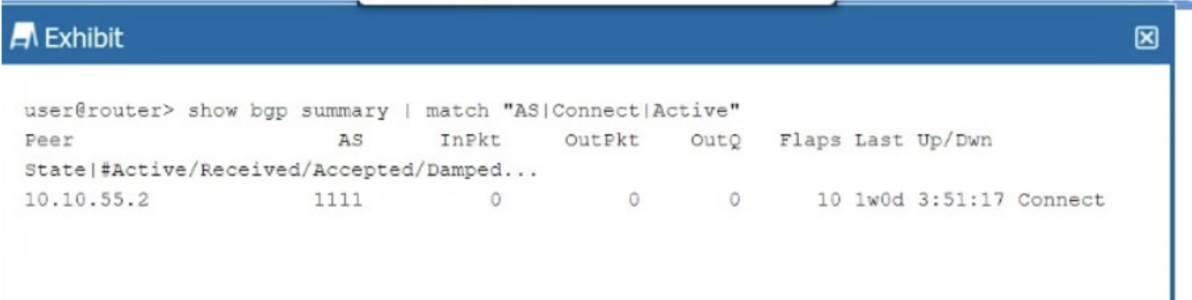
Referring to the exhibit, what is the cause of the problem?
Correct Answer:C
The BGP session in the exhibit shows the state as Connect, which indicates that the TCP session between the BGP peers has not been fully established.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
BGP State 'Connect':
The Connect state is the second stage in the BGP finite state machine (FSM). At this stage, BGP is trying to establish a TCP session with the peer, but the session has not yet been successfully established.
A successful TCP three-way handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) is required before BGP can progress to the OpenSent state, where the peers exchange BGP Open messages.
Possible Causes:
A firewall blocking TCP port 179.
Incorrect IP addresses or network connectivity issues between the BGP peers.
Juniper Reference:
BGP Troubleshooting: In Junos, if a BGP session is stuck in the Connect state, the issue is likely due to a failure in establishing the underlying TCP connection.