Exhibit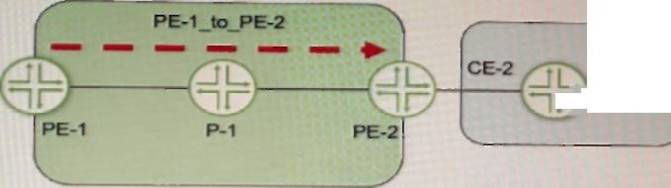
Referring to the exhibit, a working L3VPN exists that connects VPN-A sites CoS is configured correctly to match on the MPLS EXP bits of the LSP, but when traffic is sent from Site-1 to Site-2, PE-2 is not classifying the traffic correctly
What should you do to solve the problem?
Correct Answer:A
The explicit-null statement enables the PE router to send an MPLS label with a value of 0 (explicit null) instead of an IP header for packets destined to the VPN customer sites. This allows the penultimate hop router (the router before the egress PE router) to preserve the EXP bits of the MPLS label and pass them to the egress PE router. The egress PE router can then use these EXP bits to classify the traffic according to the CoS policy2. In this example, PE-1 should configure the explicit-null statement under [edit protocols mpls label-switched-path PE-1_to_PE-2] hierarchy level.
Which two statements are correct regarding bootstrap messages that are forwarded within a PIM sparse mode domain? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BD
Bootstrap messages are PIM messages that are used to distribute rendezvous point (RP) information dynamically during an RP election. Bootstrap messages are sent by bootstrap routers (BSRs), which are routers that are elected to perform the RP discovery function for a PIM sparse-mode domain. Bootstrap messages contain information about candidate RPs and their multicast groups, as well as BSR priority and hash mask length. Bootstrap messages are forwarded to all routers within a PIM sparse-mode domain using hop-by-hop flooding.
Which two statements are correct about IS-IS interfaces? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:BD
IS-IS supports two levels of routing: Level 1 (intra-area) and Level 2 (interarea). An IS-IS router can be either Level 1 only, Level 2 only, or both Level 1 and Level 2. A router that is both Level 1 and Level 2 is called a Level 1-2 router. A Level 1-2 router sends separate hello messages for each level on both point-to-point and broadcast interfaces1. A point-to-point interface provides a connection between a single source and a single destination. A broadcast interface behaves as if the router is connected to a LAN.
Exhibit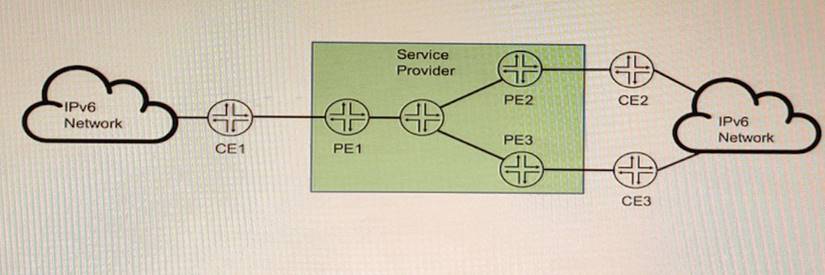
You are running a service provider network and must transport a customer's IPv6 traffic across your IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP You have already configured mpis ipv6- tunneling on your PE routers.
Which two statements are correct about the BGP configuration in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AB
To transport IPv6 traffic over an IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP, you need to configure two address families: family inet6 labeled-unicast and family inet6 unicast. The former is used to exchange IPv6 routes with MPLS labels between PE routers, and the latter is used to exchange IPv6 routes without labels between PE and CE routers. The mpis ipv6-tunneling command enables the PE routers to encapsulate the IPv6 packets with an MPLS label stack and an IPv4 header before sending them over the MPLS network.
Which two EVPN route types are used to advertise a multihomed Ethernet segment? (Choose two )
Correct Answer:AC
EVPN is a solution that provides Ethernet multipoint services over MPLS networks. EVPN uses BGP to distribute endpoint provisioning information and set up pseudowires between PE devices. EVPN uses different route types to convey different information in the control plane. The following are the main EVPN route types:
✑ Type 1 - Ethernet Auto-Discovery Route: This route type is used for network-wide messaging and discovery of other PE devices that are part of the same EVPN instance. It also carries information about the redundancy mode and load balancing algorithm of the PE devices.
✑ Type 2 - MAC/IP Advertisement Route: This route type is used for MAC and IP address learning and advertisement between PE devices. It also carries information about the Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) and the label for forwarding traffic to the MAC or IP address.
✑ Type 3 - Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag Route: This route type is used for broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic forwarding. It also carries information about the multicast group and the label for forwarding BUM traffic.
✑ Type 4 - Ethernet Segment Route: This route type is used for multihoming scenarios, where a CE device is connected to more than one PE device. It also carries information about the ESI and the designated forwarder (DF) election process.