Which two statements are correct about the customer interface in an LDP-signaled pseudowire? (Choose two)
Correct Answer:CD
The customer interface in an LDP-signaled pseudowire is the interface on the PE router that connects to the CE device. An LDP-signaled pseudowire is a type of Layer 2 circuit that uses LDP to establish a point-to-point connection between two PE routers over an MPLS network. The customer interface can have different encapsulation types depending on the type of traffic that is carried over the pseudowire. The encapsulation types are ethernet-ccc, vlan-ccc, extended-vlan-ccc, atm-ccc, frame-relay- ccc, ppp-ccc, cisco-hdlc-ccc, and tcc-ccc. Depending on the encapsulation type, the customer interface can accept or reject tagged or untagged frames in the data plane, and include or exclude VLAN tags in the control plane LDP advertisement. The following table summarizes the behavior of different encapsulation types:
Exhibit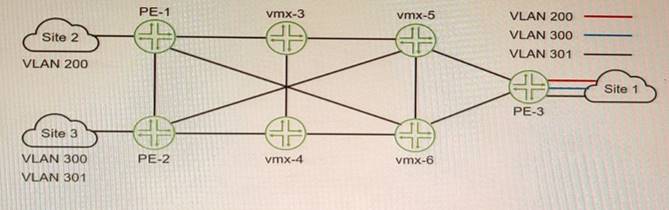
You want Site 1 to access three VLANs that are located in Site 2 and Site 3 The customer- facing interface on the PE-1 router is configured for Ethernet-VLAN encapsulation.
What is the minimum number of L2VPN routing instances to be configured to accomplish this task?
Correct Answer:B
To allow Site 1 to access three VLANs that are located in Site 2 and Site 3, you need to configure three L2VPN routing instances on PE-1, one for each VLAN. Each L2VPN routing instance will have a different VLAN ID and a different VNI for VXLAN encapsulation. Each L2VPN routing instance will also have a different vrf-target export value to identify which VPN routes belong to which VLAN. This way, PE-1 can forward traffic from Site 1 to Site 2 and Site 3 based on the VLAN tags and VNIs.
Exhibit
Which two statements are true about the OSPF adjacency displayed in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AB
The hello interval is the time interval between two consecutive hello packets sent by an OSPF router on an interface. The dead interval is the time interval after which a neighbor is declared down if no hello packets are received from it. These parameters must match between two OSPF routers for them to form an adjacency. In the exhibit, router R1 has a hello interval of 10 seconds and a dead interval of 40 seconds, while router R2 has a hello interval of 30 seconds and a dead interval of 120 seconds. This causes a mismatch and prevents them from becoming neighbors23.
When using OSPFv3 for an IPv4 environment, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:C
OSPFv3 is an extension of OSPFv2 that supports IPv6 routing and addressing. OSPFv3 is not backward compatible with IPv4 because it uses a different packet format and a different link-state advertisement (LSA) structure than OSPFv2. OSPFv3 also uses IPv6 link-local addresses as router IDs and neighbor addresses, instead of IPv4 addresses. To use OSPFv3 for an IPv4 environment, you need to enable the IPv4 unicast address family under [edit protocols ospf3] hierarchy level and configure IPv4 addresses on the interfaces.
Exhibit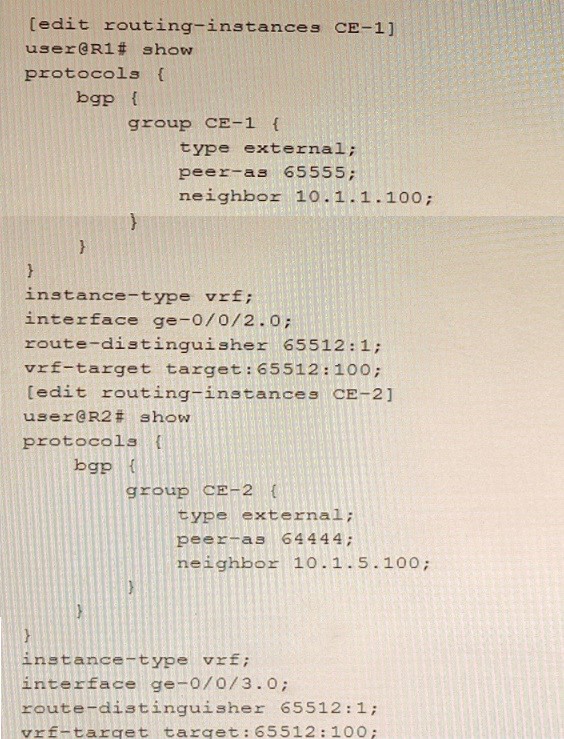
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:C
The route distinguisher (RD) is a BGP attribute that is used to create unique VPN IPv4 prefixes for each VPN in an MPLS network. The RD is a 64-bit value that consists of two parts: an administrator field and an assigned number field. The administrator field can be an AS number or an IP address, and the assigned number field can be any arbitrary value chosen by the administrator. The RD is prepended to the IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix that can be advertised across the MPLS network without causing any overlap or conflict with other VPNs. In this question, we have two PE routers (PE-1 and PE-2) that are connected to two CE devices (CE-1 and CE-2) respectively. PE-1 and PE-2 are configured with VRFs named Customer-A and Customer-B respectively.