Exhibit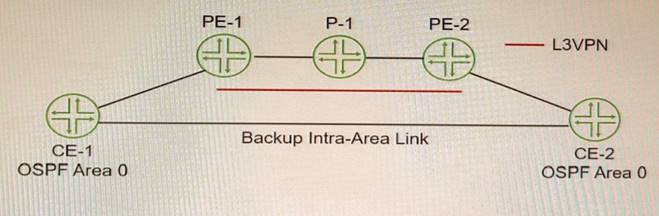
You must ensure that the VPN backbone is preferred over the back door intra-area link as long as the VPN is available. Referring to the exhibit, which action will accomplish this task?
Correct Answer:D
A sham link is a logical link between two PE routers that belong to the same OSPF area but are connected through an L3VPN. A sham link makes the PE routers appear as if they are directly connected, and prevents OSPF from preferring an intra-area back door link over the VPN backbone. To create a sham link, you need to configure the local and remote addresses of the PE routers under the [edit protocols ospf area area-id] hierarchy level1.
Exhibit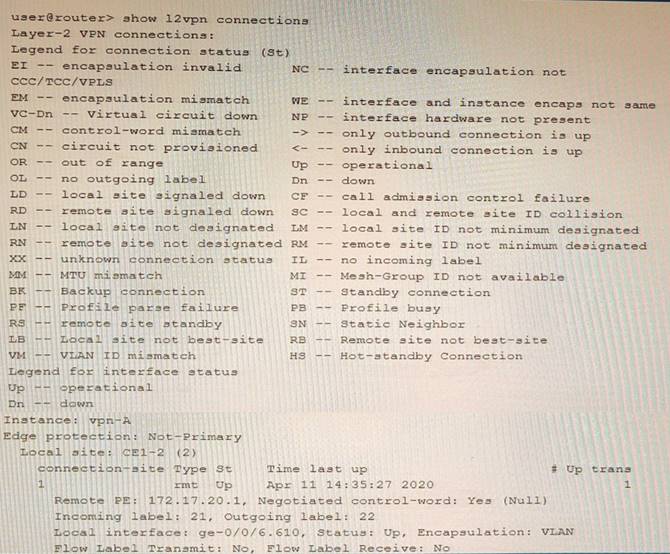
Which two statements about the output shown in the exhibit are correct? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:AD
According to 1 and2, BGP Layer 2 VPNs use BGP to distribute endpoint provisioning information and set up pseudowires between PE devices. BGP uses the Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) Routing Information Base (RIB) to store endpoint provisioning information, which is updated each time any Layer 2 virtual forwarding instance (VFI) is configured. The prefix and path information is stored in the L2VPN database, which allows BGP to make decisions about the best path.
In the output shown in the exhibit, we can see some information about the L2VPN RIB and the pseudowire state. Based on this information, we can infer the following statements:
✑ The PE is attached to a single local site. This is correct because the output shows only one local site ID (1) under the L2VPN RIB section. A local site ID is a unique identifier for a site within a VPLS domain. If there were multiple local sites attached to the PE, we would see multiple local site IDs with different prefixes.
✑ The connection has not flapped since it was initiated. This is correct because the output shows that the uptime of the pseudowire is equal to its total uptime (1w6d). This means that the pseudowire has been up for one week and six days without any interruption or flap.
✑ There has been a VLAN ID mismatch. This is not correct because the output shows that the remote and local VLAN IDs are both 0 under the pseudowire state section. A VLAN ID mismatch occurs when the remote and local VLAN IDs are different, which can cause traffic loss or misdelivery. If there was a VLAN ID mismatch, we would see different values for the remote and local VLAN IDs.
✑ The PE router has the capability to pop flow labels. This is correct because the output shows that the flow label pop bit is set under the pseudowire state section. The flow label pop bit indicates that the PE router can pop (remove) the MPLS flow label from the packet before forwarding it to the CE device. The flow label is an optional MPLS label that can be used for load balancing or traffic engineering purposes.
Your organization manages a Layer 3 VPN for multiple customers To support advanced route than one BGP community on advertised VPN routes to remote PE routers.
Which routing-instance configuration parameter would support this requirement?
Correct Answer:C
The vrf-target export parameter is used to specify one or more BGP extended community attributes that are attached to VPN routes when they are exported from a VRF routing instance to remote PE routers. This parameter allows you to control which VPN routes are accepted by remote PE routers based on their import policies. You can specify more than one vrf-target export value for a VRF routing instance to support advanced route filtering or route leaking scenarios.
In which two ways does OSPF prevent routing loops in multi-area networks? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:CD
OSPF is an interior gateway protocol that uses link-state routing to exchange routing information among routers within a single autonomous system. OSPF prevents routing loops in multi-area networks by using two methods: area hierarchy and SPF algorithm. Area hierarchy is the concept of dividing a large OSPF network into smaller areas that are connected to a backbone area (area 0). This reduces the amount of routing information that each router has to store and process, and also limits the scope of link-state updates within each area. All areas are required to connect to area 0 either directly or through virtual links2. SPF algorithm is the method that OSPF uses to calculate the shortest path to each destination in the network based on link-state information. The SPF algorithm runs on each router and builds a shortest-path tree that represents the topology of the network from the router’s perspective. The SPF algorithm prunes looped paths within an area by choosing only one best path for each destination3.
References: 2: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/ospf/topics/concept/ospf-area- overview.html 3: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/ospf/topics/concept/ospf-spf- algorithm-overview.html