What is a best practice when building System APIs?
Correct Answer:B
Correct Answer:: Model all API resources and methods to closely mimic the operations of the backend system.
*****************************************
>> There are NO fixed and straight best practices while opting data models for APIs. They are completly contextual and depends on number of factors. Based upon those factors, an enterprise can choose if they have to go with Enterprise Canonical Data Model or Bounded Context Model etc.
>> One should NEVER expose the technical details of API implementation to their API clients. Only the API interface/ RAML is exposed to API clients.
>> It is true that the RAML definitions of APIs should be as detailed as possible and should reflect most of the documentation. However, just that is NOT enough to call your API as best documented API. There should be even more documentation on Anypoint Exchange with API Notebooks etc. to make and create a developer friendly API and repository..
>> The best practice always when creating System APIs is to create their API interfaces by modeling their resources and methods to closely reflect the operations and functionalities of that backend system.
Which of the following sequence is correct?
Correct Answer:B
Correct Answer:: API Consumer requests access to API >> API Client implementes logic to call an API >> API routes the request to >> API Implementation
*****************************************
>> API consumer does not implement any logic to invoke APIs. It is just a role. So, the option stating "API Consumer implementes logic to call an API" is INVALID.
>> API Implementation does not route any requests. It is a final piece of logic where functionality of target systems is exposed. So, the requests should be routed to the API implementation by some other entity. So, the options stating "API Implementation routes the request to >> API" is INVALID
>> The statements in one of the options are correct but sequence is wrong. The sequence is given as "API Client implementes logic to call an API >> API Consumer requests access to API >> API routes the request to
>> API Implementation". Here, the statements in the options are VALID but sequence is WRONG.
>> Right option and sequence is the one where API consumer first requests access to API on Anypoint Exchange and obtains client credentials. API client then writes logic to call an API by using the access client credentials requested by API consumer and the requests will be routed to API implementation via the API which is managed by API Manager.
Select the correct Owner-Layer combinations from below options
Correct Answer:C
Correct Answer::
* 1. App Developers owns and focuses on Experience Layer APIs
* 2. LOB IT owns and focuses on Process Layer APIs
* 3. Central IT owns and focuses on System Layer APIs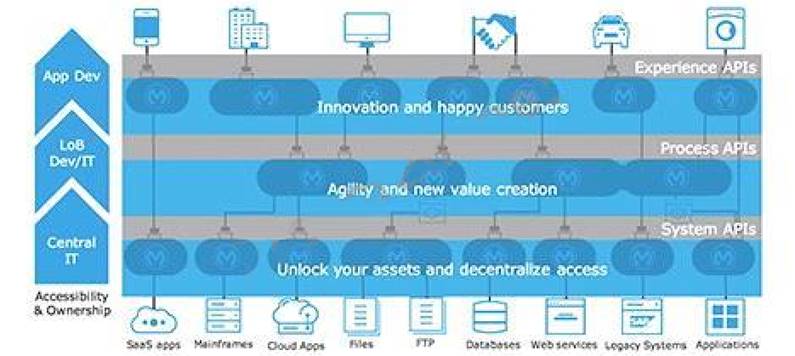
References:
https://blogs.mulesoft.com/biz/api/experience-api-ownership/ https://blogs.mulesoft.com/biz/api/process-api-ownership/ https://blogs.mulesoft.com/biz/api/system-api-ownership/
A Mule application exposes an HTTPS endpoint and is deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud. All traffic to that Mule application must stay inside the AWS VPC.
To what TCP port do API invocations to that Mule application need to be sent?
Correct Answer:D
Correct Answer:: 8082
*****************************************
>> 8091 and 8092 ports are to be used when keeping your HTTP and HTTPS app private to the LOCAL VPC respectively.
>> Above TWO ports are not for Shared AWS VPC/ Shared Worker Cloud.
>> 8081 is to be used when exposing your HTTP endpoint app to the internet through Shared LB
>> 8082 is to be used when exposing your HTTPS endpoint app to the internet through Shared LB So, API invocations should be sent to port 8082 when calling this HTTPS based app.
References:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/cloudhub-networking-guide https://help.mulesoft.com/s/article/Configure-Cloudhub-Application-to-Send-a-HTTPS-Request-Directly-to-An https://help.mulesoft.com/s/question/0D52T00004mXXULSA4/multiple-http-listerners-on-cloudhub-one-with-p
A system API has a guaranteed SLA of 100 ms per request. The system API is deployed to a primary environment as well as to a disaster recovery (DR) environment, with different DNS names in each environment. An upstream process API invokes the system API and the main goal of this process API is to respond to client requests in the least possible time. In what order should the system APIs be invoked, and what changes should be made in order to speed up the response time for requests from the process API?
Correct Answer:A
Correct Answer:: In parallel, invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment and the system API deployed to the DR environment, and ONLY use the first response.
*****************************************
>> The API requirement in the given scenario is to respond in least possible time.
>> The option that is suggesting to first try the API in primary environment and then fallback to API in DR environment would result in successful response but NOT in least possible time. So, this is NOT a right choice of implementation for given requirement.
>> Another option that is suggesting to ONLY invoke API in primary environment and to add timeout and retries may also result in successful response upon retries but NOT in least possible time. So, this is also NOT a right choice of implementation for given requirement.
>> One more option that is suggesting to invoke API in primary environment and API in DR environment in parallel using Scatter-Gather would result in wrong API response as it would return merged results and moreover, Scatter-Gather does things in parallel which is true but still completes its scope only on finishing all routes inside it. So again, NOT a right choice of implementation for given requirement
The Correct choice is to invoke the API in primary environment and the API in DR environment parallelly, and using ONLY the first response received from one of them.