Joseph works as the project manager of the NHQ Project. He has created the project network diagram as shown in the figure: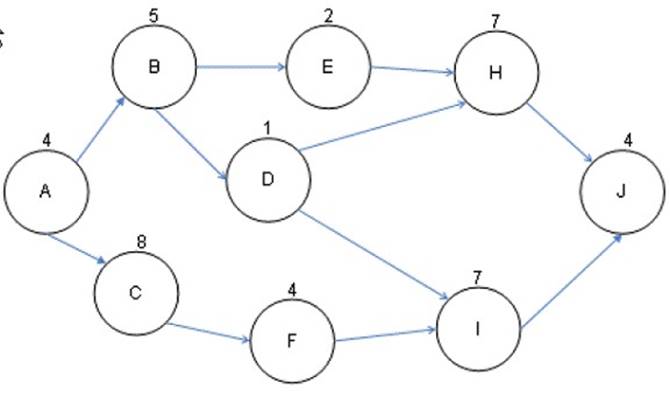
Based on the network diagram, find out which path is the critical path for this project?
Correct Answer:D
The critical path is the path with the longest duration to complete the project. It has no float and shows the earliest completion date and the latest completion date for the project. In this example, path ACFIJ takes 27 days and is the critical path.
ACFIJ= A(4)+C(8)+F(4)+I(7)+J(4)= 27
A critical path is the sequence of project activities, which add up to the longest overall duration. This determines the shortest time possible to complete the project. Any delay of an activity on the critical path directly impacts the planned project completion date (i.e. there is no float on the critical path). A project can have several, parallel, near critical paths. An additional parallel path through the network with the total durations shorter than the critical path is called a sub-critical or non-critical path. These results allow managers to prioritize activities for the effective management of project completion, and to shorten the planned critical path of a project by pruning critical path activities, by "fast tracking" (i.e., performing more activities in parallel), and/or by "crashing the critical path" (i.e., shortening the durations of critical path activities by adding resources).
Answer option A is incorrect. ABEHJ takes only 22 days to complete.
ABEHJ= A(4)+B(5)+E(2)+H(7)+J(4)= 22
Answer option C is incorrect. ABDHJ takes 21 days to complete. ABDHJ= A(4)+B(5)+D(1)+H(7)+J(4)= 21
Answer option B is incorrect. ABDIJ takes 21 days to complete. ABDIJ= A(4)+B(5)+D(1)+I(7)+J(4)= 21
What forecasting method would your project use if your project customer requires an autoregressive moving average for performance forecasting?
Correct Answer:D
The autoregressive moving average is an example of a causal/econometric method for the forecasting project performance. The casual/econometric forecasting method uses the assumption that it is possible to identify the underlying factors, which might influence the
variable being forecasted. For example, sales of umbrellas might be associated with weather conditions. If the causes are understood, projections of the influencing variables can be made and used in the forecast. Some examples of casual/econometric forecasting method are as follows: Regression analysis using linear regression or non-linear regression Autoregressive moving average (ARMA) Autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) Econometrics
Answer option B is incorrect. The time series method relies on the earned value, moving average, extrapolation, and growth curve.
Answer option A is incorrect. The judgmental methods use intuition, the Delphi method, and forecast by analogy.
Answer option C is incorrect. The ensemble forecasting is not part of the causal/econometric method for forecasting.
Kelly is the project manager of her organization. She is reviewing the project network diagram to confirm that the resource she has identified is available to complete the project assignments without conflicting with other activities in the project node. The availability of resources will help Kelly determine the final finish date for the project. What scheduling technique is Kelly using?
Correct Answer:A
The Critical Chain method examines the availability of project resources to determine when
the resource may be utilized without conflicting with other activities. The Critical Chain method is a project management technique in which schedule network analysis is used for the purpose of modifying and determining a set of project schedules to account for more inadequate than estimated project financial resources. This method tends to keep the resources levelly loaded, but requires the resources to be flexible in their start times and to quickly switch between tasks and task chains to keep the whole project on schedule. In the Critical Chain method, projects are completed more rapidly and with better scheduling consistency.
Answer option C is incorrect. The Critical Path method examines the duration of the critical path to determine the finish date for the project. It does not consider when project activities are available.
Answer option B is incorrect. Resource utilization simply means that the resource is scheduled for work.
Answer option D is incorrect. A resource leveling heuristic is a guideline, such as a maximum of 35 hours per week, per resource. It is a rule that usually signals the maximum amount of hours a resource may be utilized on the project.
Robert is the project manager for his organization. Management has asked Robert to provide them with the metric he uses to measure deliverables status, costs incurred, and especially how he measures the schedule progress for schedule adherence. What project component could Robert provide for management?
Correct Answer:C
Work performance measurements are metrics that are defined to collect performance and progress of the project. Typical metrics are deliverables, schedule, and costs, though additional metrics, such as quality, can be added. Work performance measurements are created from the work performance information. WPMs are an output of Control schedule, Control cost, and Control scope processes, which are monitoring and controlling processes. WPMs consist of planned versus actual performance indicators with respect to scope, schedule, and cost. They are documented and communicated to the stakeholders and are used to make project activity metrics, such as the following: Planned vs. Actual Technical performance and Scope performance Planned vs. Actual Schedule performance Planned vs. Actual Cost performance
Answer option D is incorrect. The project management plan is too broad and is not the best choice.
Answer option B is incorrect. The cost management plan and the project schedule would not provide all the information that management has requested.
Answer option A is incorrect. The milestone list does not include performance metrics.
Mary is the project manager for her company. She's working with the project team to compress the project schedule as the project must be completed by December 30. For some of the project activities, she and the project team have agreed to crash the project work. What must be true of these project activities for crashing to be acceptable?
Correct Answer:B
Crashing is the addition of project resources to complete effort-driven activities in faster time. By adding more labor the activity can be completed faster. Crashing is a schedule compression technique to obtain the greatest amount of compression for the least incremental cost. Crashing works for activities where additional resources will shorten the duration. Approving overtime, bringing in additional resources, paying to expedite delivery to activities on the critical path are examples of crashing.
Answer option A is incorrect. An activity of fixed duration, such as printing 100,000 brochures in a printing press, won't be completed faster by adding more effort. Answer option D is incorrect. Activities need not be risk-free to use project crashing. Answer option C is incorrect. All effort-driven activities are susceptible to the Law of
Diminishing Returns. By adding more labor the value of the yield of the work decreases because of the cost of the labor added to the project work.