Which of the group creativity techniques enhances brainstorming with a voting process used to rank the most useful ideas for further brainstorming or prioritization?
Correct Answer:C
The various group creativity techniques are as follows: Brainstorming: It is a technique used to generate and collect multiple ideas related to the project and product requirements. Nominal group technique: It is a technique used to enhance brainstorming with a voting process used to rank the most useful ideas for further brainstorming or prioritization. Delphi technique: It is a techniques used to identify potential risk. In this technique, the responses are gathered via a questionnaire from different experts and their inputs are organized according to their contents. Idea/mind mapping: It is a technique used to map the ideas generated by brainstorming to reflect the commonality and differences in understanding and generating new ideas. Affinity diagram: It is a technique used to allow a large number of ideas to be sorted into groups for review and analysis.
Harry works as the project manager for his organization. He is creating the activity list and would like to tag those activities that are comprised of apportioned effort. Which of the following is the best example of apportioned effort?
Correct Answer:B
Apportioned effort is effort applied that you cannot subdivide into work packages, but it is related to, usually in a supportive role, to the completion of the project work packages. The project management overhead, such managing the project work, is an example of apportioned effort. Apportioned effort (AE) is the effort that is applied to the project-related work that cannot be easily and readily divided into discrete efforts for those tasks, but which is associated in a direct proportion to the discrete work efforts that are capable of being measured. The presence of apportioned effort relies particularly on the performance of further efforts.
Answer option C is incorrect. This is an example of discrete effort.
Answer option A is incorrect. This is an example of a scope change that has not been approved.
Answer option D is incorrect. This is an example of a scheduling technique.
You are the project manager for your organization. You want to record some details about the work that the project team has to complete. You want to document the level of effort, where the work is to be performed, and the person who will be responsible for completing the work. Which of the following is the best place to document this information?
Correct Answer:A
The activity attributes initially include the Activity ID, WBS ID, and the Activity Name, but it can evolve over time to include other components about the work. Activity attributes are an output of the Define Activity process. These attributes refer to the multiple components that frame up an activity. The components for each activity during the early stages of the project are the Activity ID, WBS ID, and Activity name. At the later stages, the activity attributes include Activity codes, Predecessor activity, activity description, logical relationship, successor activity, leads and lags, imposed dates, and constraints and assumptions. Activity attributes are used for schedule development and for ordering, selecting, and sorting the planned schedule activities in a number of ways within reports.
Answer option B is incorrect. A project management plan is a formal document that defines how the project is being monitored, controlled, and executed. It is not the best answer. Answer option D is incorrect. The roles and responsibilities matrix records the work and the person to record the work, but does not offer additional information such as locale for the work, level of effort, and other information.
Answer option C is incorrect. The Schedule Management Plan defines how the schedule will be created, executed, and controlled.
Kay is the project manager of the QUI Project. This project is done but is also considerably over budget. Kay has elected to crash the project in order to recoup schedule delays but this increased the project costs. What should Kay do with the information regarding the schedule delays and cost overruns?
Correct Answer:A
When there have been significant corrective action decisions the reasoning behind the decision should be documented in the lessons learned documentation. What is lessons learned documentation? Lessons learned documentation is prepared to contribute to the lessons learned knowledge database of the organization. It includes the causes of issues, the reasoning behind the corrective action chosen, and other types of lessons learned about stakeholder management. Lessons learned are documented so that they become part of the historical database for the project/program and the performing organization. The lessons learned are compiled, formalized, and stored through out the project's/program's duration.
Answer option C is incorrect. A variance report may be appropriate but cost and schedule variances are reported differently. Kay could create a cost variance report and a schedule variance report, but not one report for both project attributes.
Answer option B is incorrect. An exceptions report is the same as a variance report. Kay would create a separate exceptions report for cost, and another for schedule.
Answer option D is incorrect. The information may go into the project final report but it should be included in the project's lessons learned information when it is discovered.
You are the project manager of the GHQ Project. You have to prioritize activities for the effective management of project. For this, you have created a network diagram to schedule a set of project activities as shown in the figure: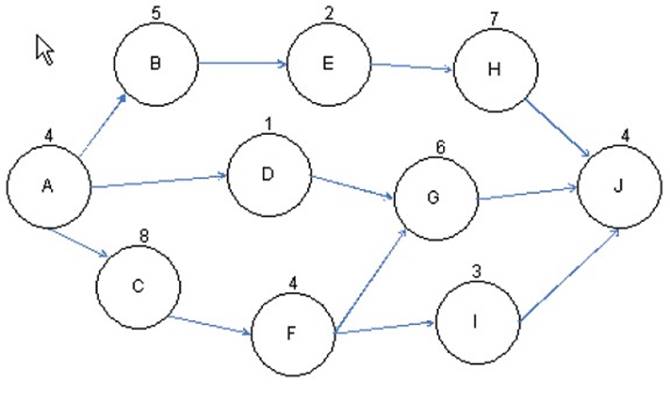
Based on this figure, what is the critical path of this project?
Correct Answer:D
The activity nodes of path ACFGJ equals 26 days and is the longest path to completion - it is the critical path.
ACFGJ= A(4)+C(8)+F(4)+G(6)+J(4)=26
What is a critical path?
A critical path is the sequence of project activities, which add up to the longest overall duration. This determines the shortest time possible to complete the project. Any delay of an activity on the critical path directly impacts the planned project completion date (i.e. there is no float on the critical path). A project can have several, parallel, near critical paths. An additional parallel path through the network with the total durations shorter than the critical path is called a sub-critical or non-critical path. These results allow managers to prioritize activities for the effective management of project completion, and to shorten the planned critical path of a project by pruning critical path activities, by "fast tracking" (i.e., performing more activities in parallel), and/or by "crashing the critical path" (i.e., shortening the durations of critical path activities by adding resources).
Answer option A is incorrect. ABEHJ takes only 22 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ABEHJ=A(4)+B(5)+E(2)+H(7)+J(4)=22
Answer option C is incorrect. ADGJ takes only 15 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ADGJ=A(4)+D(1)+G(6)+J(4)=15
Answer option B is incorrect. ACFIJ takes only 23 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ACFIJ=A(4)+C(8)+F(4)+I(3)+J(4)=23