- (Exam Topic 2)
Which of the following is a primary security concern for a company setting up a BYOD program?
Correct Answer:D
Jailbreaking is a process of bypassing or removing the manufacturer-imposed restrictions on a mobile device’s operating system, allowing users to install unauthorized applications, modify settings, etc. It is a primary security concern for setting up a BYOD program because it can expose the device and its data to malware, vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, etc.
- (Exam Topic 2)
A company is focused on reducing risks from removable media threats. Due to certain primary applications, removable media cannot be entirely prohibited at this time. Which of the following best describes the company's approach?
Correct Answer:C
Mitigating controls are designed to reduce the impact or severity of an event that has occurred or is likely to occur. They do not prevent or detect the event, but rather limit the damage or consequences of it. For example, a backup system is a mitigating control that can help restore data after a loss or corruption.
In this case, the company is focused on reducing risks from removable media threats, which are threats that can compromise data security, introduce malware infections, or cause media failure123. Removable media threats can be used to bypass network defenses and target industrial/OT environments2. The company cannot prohibit removable media entirely because of certain primary applications that require them, so it implements mitigating controls to lessen the potential harm from these threats.
Some examples of mitigating controls for removable media threats are:  Encrypting data on removable media
Encrypting data on removable media Scanning removable media for malware before use
Scanning removable media for malware before use  Restricting access to removable media ports
Restricting access to removable media ports Implementing policies and procedures for removable media usage and disposal
Implementing policies and procedures for removable media usage and disposal  Educating users on the risks and best practices of removable media
Educating users on the risks and best practices of removable media
- (Exam Topic 2)
A user reports constant lag and performance issues with the wireless network when working at a local coffee shop A security analyst walks the user through an installation of Wireshark and gets a five-minute pcap to analyze. The analyst observes the following output: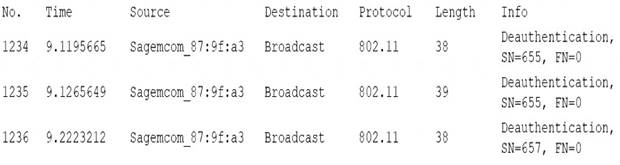
Which of the following attacks does the analyst most likely see in this packet capture?
Correct Answer:B
An evil twin is a type of wireless network attack that involves setting up a rogue access point that mimics a legitimate one. It can trick users into connecting to the rogue access point instead of the real one, and then intercept or modify their traffic, steal their credentials, launch phishing pages, etc. In this packet capture, the analyst can see that there are two access points with the same SSID (CoffeeShop) but different MAC addresses (00:0c:41:82:9c:4f and 00:0c:41:82:9c:4e). This indicates that one of them is an evil twin that is trying to impersonate the other one.
- (Exam Topic 2)
A company wants to deploy decoy systems alongside production systems in order to entice threat actors and to learn more about attackers. Which of the follow r 3 best describes these systems?
Correct Answer:B
Honey pots are decoy systems or resources that are designed to attract and deceive threat actors and to learn more about their motives, techniques, etc. They can be deployed alongside production systems to create an illusion of a vulnerable target and divert attacks away from the real systems. They can also collect valuable information and evidence about the attackers and their activities for further analysis or prosecution.
- (Exam Topic 1)
A business is looking for a cloud service provider that offers a la carte services, including cloud backups, VM elasticity, and secure networking. Which of the following cloud service provider types should business engage?
Correct Answer:A
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers offer a la carte services, including cloud backups, VM elasticity, and secure networking. With IaaS, businesses can rent infrastructure components such as virtual machines, storage, and networking from a cloud service provider. References: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide, pages 233-234